Understanding OTC Deficiency
Discover the essentials of OTC deficiency, a rare condition affecting ammonia processing. Learn about diagnosis, treatment, and common misconceptions for managing this genetic disorder.
Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that disrupts the body's ability to process ammonia, a waste product produced when proteins are broken down. This condition leads to a dangerous buildup of ammonia in the bloodstream, a situation known as hyperammonemia. Ammonia is toxic, especially to the brain, and can cause serious health issues if not managed properly.
Understanding OTC Deficiency
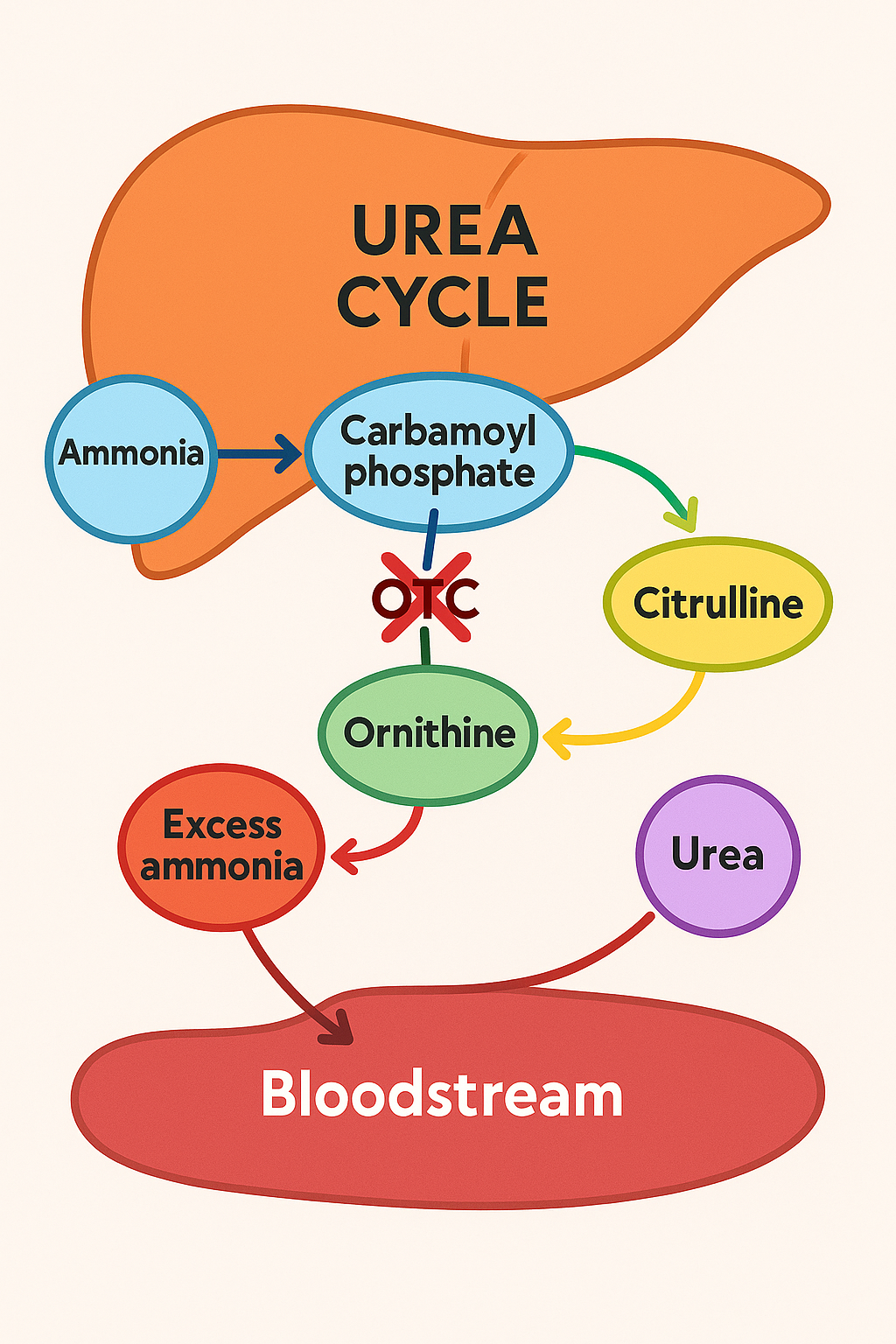
The body has a process called the urea cycle, which occurs in the liver and is responsible for converting ammonia into urea, a substance that is then excreted through urine. OTC is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in this cycle by helping convert ammonia into urea. When there's a deficiency or absence of OTC, ammonia accumulates in the blood, leading to symptoms such as vomiting, lethargy, confusion, and, in severe cases, coma or death. (medlineplus.gov)
Confirming the Diagnosis
Diagnosing OTC deficiency involves several steps:
-
Clinical Evaluation: Healthcare providers assess symptoms and medical history.
-
Blood Tests: Elevated ammonia levels in the blood can indicate a urea cycle disorder.
-
Genetic Testing: Identifying mutations in the OTC gene confirms the diagnosis. (medlineplus.gov)
Common Myths and Misconceptions
-
Myth: OTC deficiency only affects newborns.
Fact: While severe forms often present in newborns, milder forms can appear later in life, even in adulthood. (medlineplus.gov)
-
Myth: OTC deficiency is a rare condition with no known treatments.
Fact: OTC deficiency is treatable. Management includes a low-protein diet, medications to help remove excess ammonia, and, in severe cases, liver transplantation. (medlineplus.gov)
Understanding Your Diagnosis
Receiving a diagnosis of OTC deficiency means your body has difficulty processing ammonia due to a deficiency in the OTC enzyme. This condition requires ongoing management to prevent ammonia buildup and associated health issues. Treatment plans are personalized and may include dietary adjustments, medications, and regular monitoring to ensure ammonia levels remain safe. With appropriate care, individuals with OTC deficiency can lead healthy lives.